PRO-ANTIBIOTICS: PROBIOTICS FOR CONCURRENT USE WITH ANTIBIOTICS AND SUPPORTING THERAPY
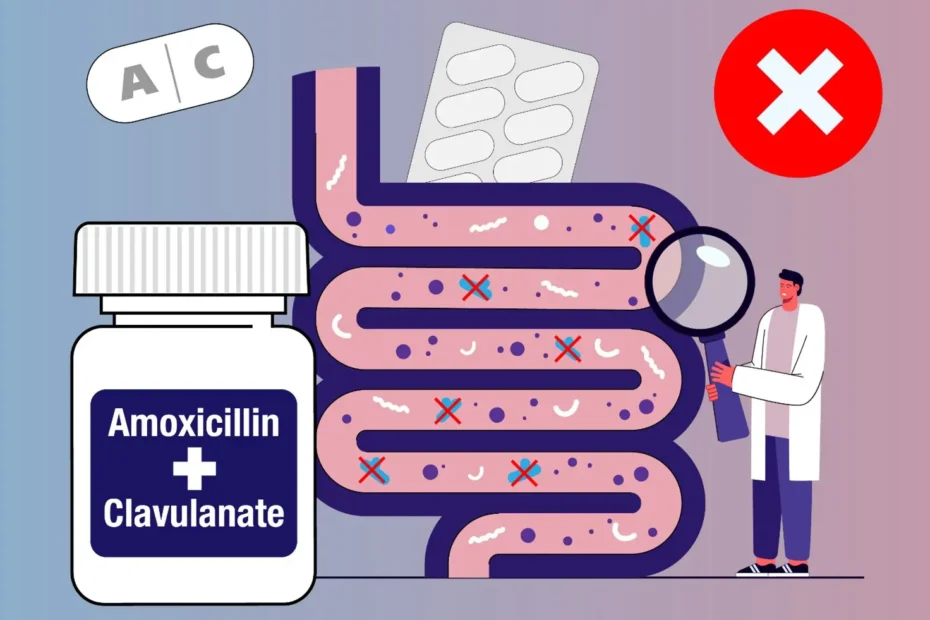
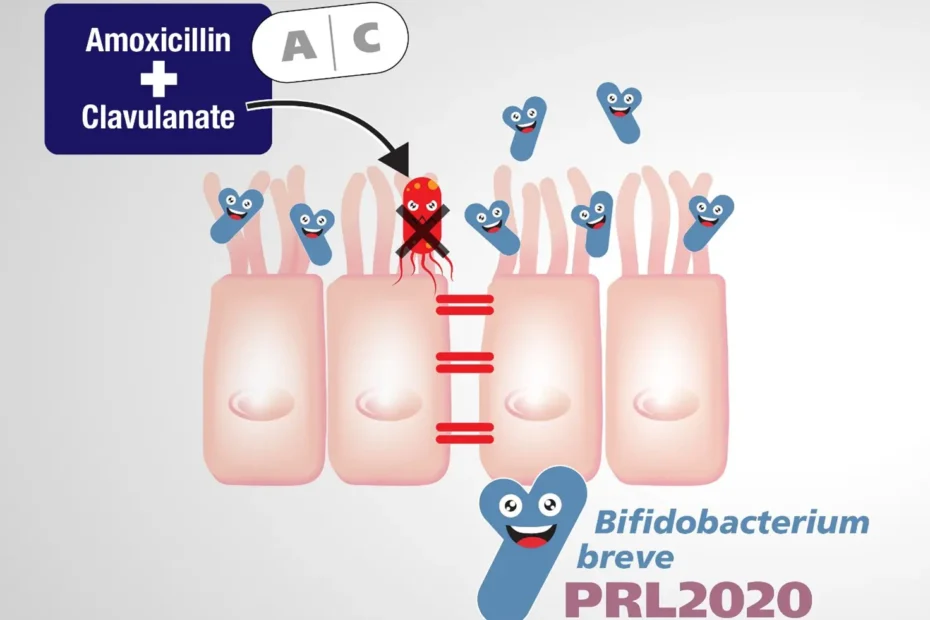
Antibiotics, while essential for eliminating pathogenic bacteria responsible for infections, act indiscriminately, also targeting commensal bacteria that help maintain the delicate balance of our gut microbiota. This often leads to a condition known as dysbiosis, a term describing an imbalance in the composition and function of the microbiota. Dysbiosis is not only a consequence of the elimination of beneficial bacteria but also opens the door to a host of associated problems.